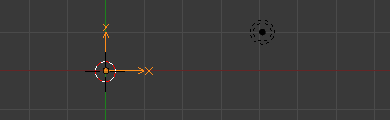
Introduction
To get depth of field in Blender, you need to set the camera up and then create a defocus node (since it’s a postprocessing effect). Here’s how.
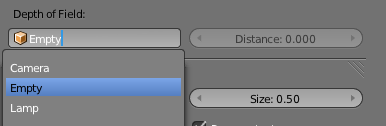
Step 3
Select the camera. In Camera, click on the Depth of Field box and select or enter the name of the empty (probably Empty).
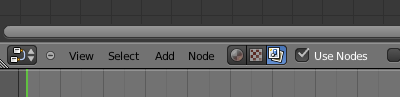
Step 4
Go to the Node Editor, click the third icon (Composite Nodes), and check the Use Nodes checkbox.
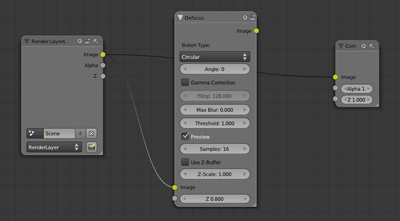
Step 5
In the Node Editor, click Add->Filter->Defocus and move the new defocus node in between your Render Layers node and your Composite node.
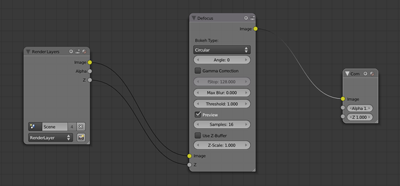
Step 6
Connect the Z output on the Render Layers node to the Z input on the Defocus node. Also connect the image output on the Defocus node to the image input on the Composite node.
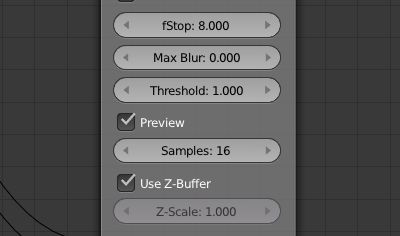
Step 7
In the Defocus node, check the Use Z-Buffer checkbox. Also set fStop down to something low (lower is blurrier) — try 8 or 12 for starters. The lower the fStop value, the blurrier the out-of-focus parts get.
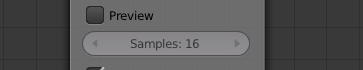
Step 8
Before you do the final render, uncheck the Preview checkbox in the Defocus node. Also, remember that depth of field is a postprocessing effect, so you won’t see the bokeh until after the render finishes.
The End.
Further Reading
- Depth of field (Wikipedia)
- Composite Defocus (Blender 2.43 docs)
- Using defocus node to get the “Depth of field” effect in blender (Vimeo)